Most Emotionally Responsive Robot
Kismet, created by Cynthia Breazeal at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), is
a robotic head powered by 15 networked computers and 21 motors. It is designed to
recognize and respond to different emotions while interacting with humans. Nine of the
computers are used to control Kismet's vision alone- Most Complex Artificial Brain
The Genobyte Corporation of Colorado, USA, with Advanced Telecommunications Research,
Japan, have developed a brain for a robot cat called Robokoneko (“Robot Kitten” in
Japanese). It will have the ability to “learn". The unit consists of millions of
artificial neurons, which in organic brains control the transmission of data and
instructions to the eyes, ears, and limbs. Initially, the connections between these
neurons are random, but in a dynamic, Darwinian-like process of evolution the robo-cat can
discard dud neural pathways and develop only successful processes.
- Fastest-Selling Entertainment Robot
The world's fastest-selling entertainment robot is the AIBO. In Japanese it means
"companion". It is also an acronym for Artifical Intelligence Robot. When AIBO
made its first appearance on Sony's website on May 31, 1999, 3,000 were sold in 20
minutes. On June 1, 1999, when 2,000 AIBOs became available over the internet in America,
the rush to buy the puppy caused web servers to crash! AIBO is 28 cm (11 in) tall and
retails for over $2,000.
- Most Lifelike Robot Fish
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries of Japan have developed a series of robotic fish. The models
are so lifelike that only the closest inspection can tell them apart from the real thing.
The project was spurred by the superb efficiency of the swimming motion of a fish.
Possible future applications include the development of submarines that could travel much
further and faster than with today's technology. The first model made in the robotic fish
project was a robotic sea bream, weighing 5.73 lb and measuring 60 cm in length. Yet the
project is mainly concerned with robotic replicas of extinct fish, for use in virtual
aquariums.
- Most Humanoid Robot
The P3 is the world's first humanoid robot that can actually walk. Pioneered by
the Japanese company Honda in 1997, the 160-cm (5-ft 3-in) tall robot has a human-like
limb configuration with a pair of arms and legs. P3 can walk sideways, backwards, up and
down stairs, and on sloped floors. The robot has 3-D vision and can also turn its head,
step over obstacles, change direction, and correct its balance if pushed. It can wave,
shake hands, and pick things up.
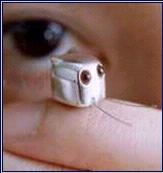
- Smallest Robot
The world's smallest robot is the Monsieur microbot, developed by the Seiko Epson
Corporation of Japan, in 1992. The light-sensitive robot is less than one cm high (0.06
in), weighs 1.5 g (0.05 oz), and is made of 97 separate watch parts - the equivalent of
two ordinary watches. The microbot won a design award at the International Contest for
Hill-Climbing Micromechanisms.
|
|
MATCH PICS AND TEXTS!! |
|
|
|
|
| A |
|
 |
|
|
| B |
|
 |
|
|
| C |
|
 |
|
|
| D |
|
 |
|
|
|